Varsha Ranganathan, B.Optom
Clinical Optometrist, Jaya Eye Care Centre, A Unit of Maxi Vision Eye Hospital, Chennai, India
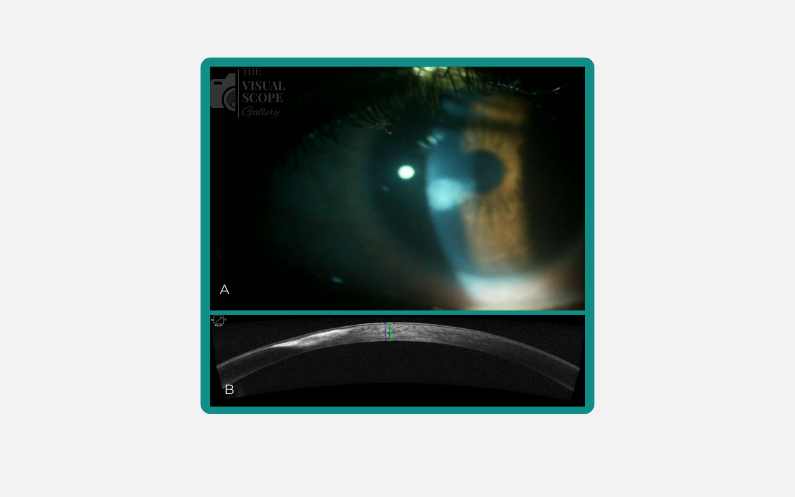
Image: : A) Corneal Opacity as seen in the Slit Lamp Examination. B) Cross-sectional view of the cornea seen via Anterior Segment OCT
Image Summary
Corneal opacity, characterised by clouding of the cornea, is a potential consequence of corneal ulcers, particularly those associated with contact lens use. Infectious corneal ulcers are a major cause of blindness globally. Risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing contact lens-related corneal ulcers include overnight lens wear, prolonged continuous use, dry eye conditions, and poor hygiene practices. Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography (AS-OCT) serves as a valuable non-invasive imaging modality for evaluating corneal opacities. It enables detailed assessment of the opacity’s location, depth, and involvement of corneal layers, thereby facilitating the evaluation of disease severity and monitoring therapeutic response.


Recent Comments